Human health is inextricably linked to animal health and production. This link between human and animal populations, and with the surrounding environment, is particularly close in developing regions where animals provide transportation, draught power, fuel and clothing as well as proteins (meat, eggs and milk). A number of animal diseases represent significant public health concern in developing countries.
In recent years, there has been increasing concern about the use of antibiotics in food-producing animals. Authorities in developing countries are now focusing on bringing in the much needed change in the way livestock products are produced and marketed.
Increasing environmental disasters and uncertainties in business environment are also cause of serious concern for livestock farmers and companies active in the sector.
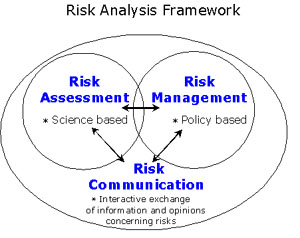
Scientific community has been advocating risk-based approaches to animal diseases and food safety in developing countries. The risk analysis framework (Lammerding, 1996) broadly focuses on three aspects e.g. Risk Assessment, Risk Management and Risk Communication.
Business Continuity Management (BCM) is a suggested tool for entrepreneurs as far as preparedness for disaster and uncertainty is concerned.
BCM is the act of anticipating incidents which will affect the mission critical functions and processes for an organization / sector as such and ensuring that the organization or the sector collectively responds to any such incident in a plan and rehearsed manner.
At Vet Helpline India, we provide consultancy to state and national level agencies in participatory risk assessment, policy analysis and development of communication strategy.
We also work with companies, farmer and trader organizations to assist them in Business Continuity Management in the context of disasters and uncertainities.